Correlation
Share
Your study cart is empty!
What is Correlation
Correlation measures the strength of linear relationship between two variables. Here two variables are measured on ratio scale of measurement. The formula of the correlation coefficient is given by:
Types of Correlation Coefficient
There a various type of correlation on basis of measurement of the scale of two variable.
| X | Y | Type of Correlation |
| Nominal | Nominal | Phi Coefficient |
| Nominal | Ordinal | Rank bi-serial Coefficient |
| Nominal | Interval | Point Bi-serial Coefficient |
| Ordinal | Ordinal | Spear-man Rank Correlation Coefficient |
| Interval | Interval | Pearson Product moment Correlation Coefficient |
t test for test the significance of Correlation Coefficient
Hypothesis
Test Statistic
Critical value
P-value
Decision rule
Does Correlation imply Causation?
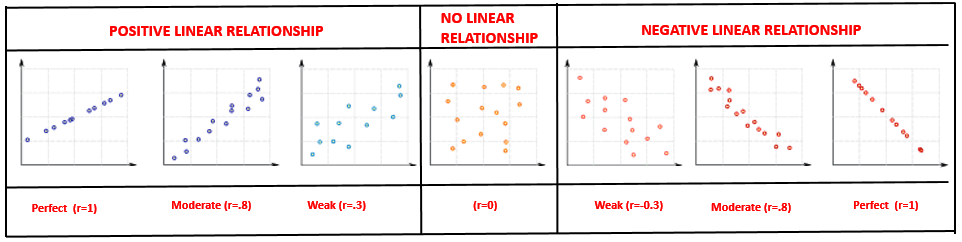
Correlation doesn’t necessarily imply causation. Correlation measures the degree of association between the two variables. Or in other words, it measures the strength of linear relationship between them. The value of correlation coefficient can lie in the interval [-1, 1]. -1 denotes a perfect negative linear relationship and +1 a perfect positive linear relationship. Values between [-0.3, 0.3] imply a very weak linear association or almost no linear relationship between the two variables. Values between [-0.7, -1] and [0.7, 1] indicates a strong linear relationship. Causation means the change in one variable is caused by other. While correlation depicts the strength of association. Positive linear relationship implies that with an increase in one variable, another variable also increases. Negative linear relationship implies that with increase in one variable, another variable decreases.
Considering two variables cigarettes and pulse rate which are highly correlated, I cannot say Cigarettes alone causes pulse rate to increase, but I am sure that there is a positive linear relationship between the two. That is as the number of cigarettes increases, the pulse rate also increases. And vice versa. There are other possible factors which cause pulse rate to increase. And the association between these variables doesn’t imply causation in statistical terms.
Developed by Versioning Solutions.







