Method of simple random sampling is used
There are only two outcomes, p (probability of success) or q (probability of failure). Also, p + q = 1
If np≥10 and nq≥10, then normal approximation to binomial is valid
Hypothesis
Ho: population proportion is equal to po. p = po
Ha1: population mean is equal to po. p≠po (Two tailed test)
Ha2: population mean is equal to po. p<po (Left tailed test)
Ha3: population mean is equal to po. p>po (Right tailed test)
Here p_o takes a particular value.
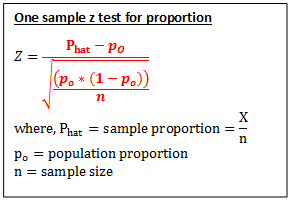
Test Statistic
Critical value
-z(a/2), z(a/2) (Two tailed test)
-z(a) (Left tailed test)
z(a) (Right tailed test)
P-value
2*(1-P(Z≤|z|) (Two tailed test)
P(Z≤z) (Left tailed test)
P(Z≥z) (Right tailed test)
Decision rule
Reject Ho if |z|>z(a/2) or p-value < alpha (two tailed test)
Reject Ho if –z < -z(a) or p-value < alpha (left tailed test)
Reject Ho if z > z(a) or p-value < alpha (right tailed test)