Question 4
The Steiner Minimum Tree Problem. Given a weighted graph G =(V,E) with weights w and a set of vertices B ⊆ V, find a tree T =(V',E') such that B ⊆ V' ⊆ V and E' ⊆ E that is of minimum total weight 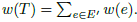
Phylogeny. Consider a set s1,...,sn of current species. A phylogeny is a tree representation of the evolution that led, from a common unique ancestor, to s1,...,sn.
The exact phylogeny is usually unknown, and it is an important problem in computational biology to find the one that is most likely. One of the prominent methods to reconstruct the phylogeny is the following: The input is given by a matrix M ∈ {0,1}nxm, where each row represents a species, and each column a character (e.g. the presence of a certain gene in the DNA, or a physical characteristic), and entry M[i,j] is 1 if species i has character j, and 0 otherwise (see Figure 2, left). Figure 2, right gives a possible phylogeny of four species (lamprey, shark, salmon, lizard). It assumes that:
(*) all the species evolved from a common ancestor species a1, where none of the characters are present, through a sequence of successive ancestors.
(**) Each species evolved from a previous ancestor species by developing one or more characters, or after one or more characters have disappeared.
(***) no two species with exactly the same characters appear at any time during the evolution.
In the tree T in Figure 2, a2 evolved from a1 by developing characters a, b, and shark, salmon, lizard evolved from the common ancestor a2. Salmon and lizard evolved from the common ancestor a3, that has characters a, b, c. Points at which characters emerge are indicated by labeled bars. A State change in T is the emergence or the disappearance of a certain character between two different species. For instance, between ancestors a1 and a2, there are two state changes. T has in total 7 state changes.
a) Find a phylogeny tree for the instance in Figure 2 that respects hypothesis (*), (**), (***) and has at least 8 state changes.
b) A most parsimonious tree is a phylogeny tree that respects conditions (*),(**), (***) and has a minimum number of state changes. Those trees are often considered very good candidates for representing the real evolution of the species. Give a weighted graph G with weights w such that the problem of finding the most parsimonious tree for the input in Figure 2, left can be formulated as a Steiner Minimum Tree problem over G.
Students succeed in their courses by connecting and communicating with an expert until they receive help on their questions

Consult our trusted tutors.